Malignant Leakage, Subsidence and Plugging Technology of Salt Bottom in front of Tarim Mountains (Part 2)
2.1.3 Evaluation of Sedimentation Rate of Sealing Slurry
The rheological properties of oil-based drilling fluids are greatly affected by temperature and oil-water ratio, and the room temperature suspension and high-temperature settling rate of the drilling fluid can be adjusted by changing the oil-water ratio.The rheological properties of oil-based drilling fluids with different oil-water ratios were tested at room temperature and 80℃, and the results are shown in Tables 3 and 4.
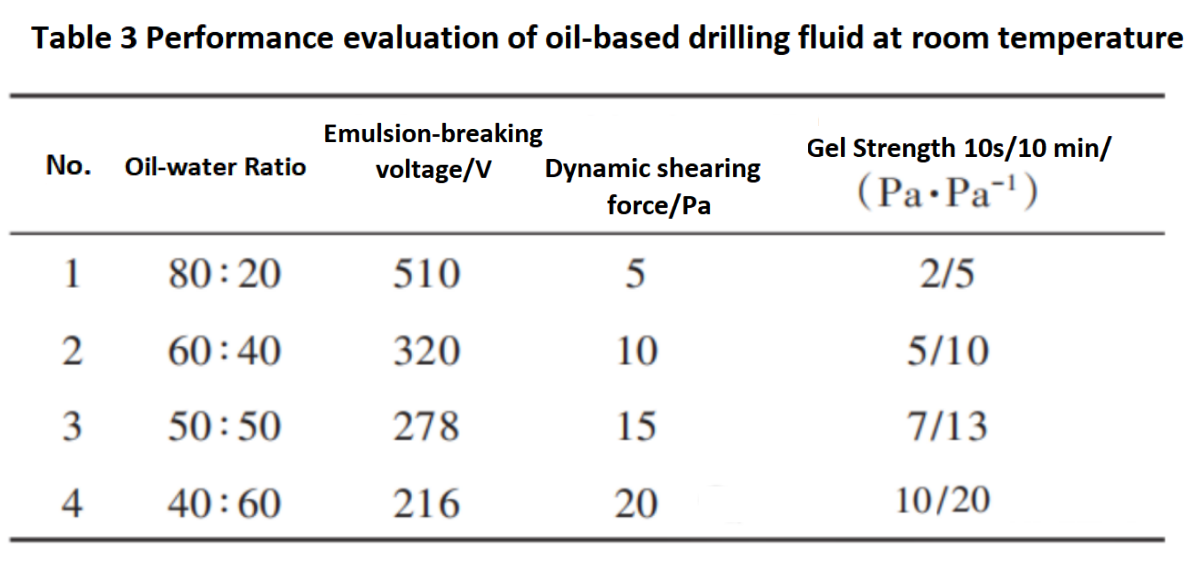
Note: 1. The well slurry formula is diesel fuel+25% CaCl2 saltwater+3% main emulsion+3% auxiliary emulsion+1% wetting agent+3% CaO+2% fluid loss agent+weighting agent (ρ=2.0 g/cm³); 2. The testing conditions are at room temperature of 25℃.
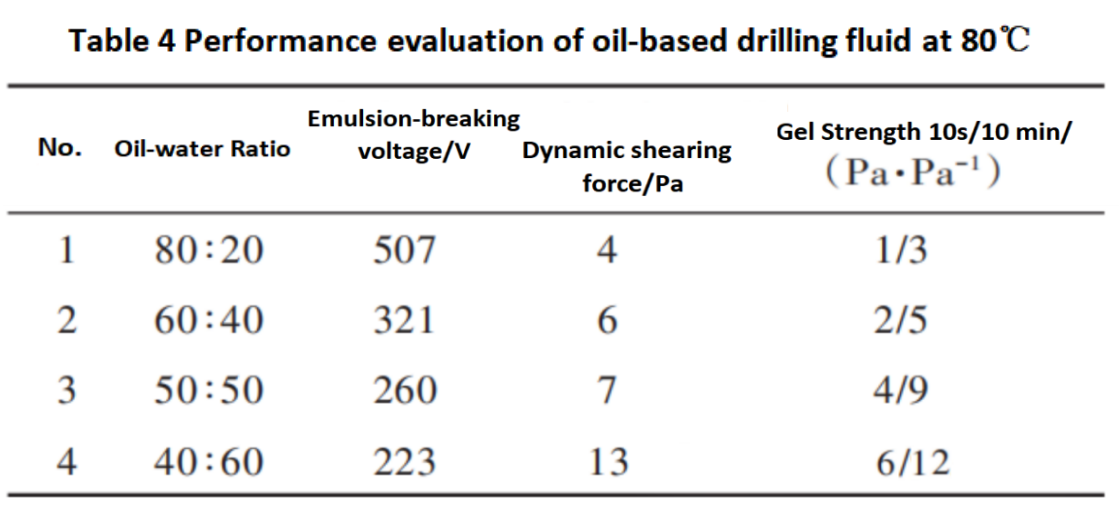
Note: The well slurry formula is diesel fuel+25% CaCl2 saltwater+3% main emulsion+3% auxiliary emulsion+1% wetting agent+3% CaO+2% fluid loss agent+weighting agent (ρ=2.0 g/cm ³).
From Tables 3 and 4, it can be seen that at room temperature, as the oil-water ratio decreases, the demulsification voltage of the oil-based drilling fluid gradually decreases, while the dynamic shear force and initial/final shear force increase, indicating a decrease in the stability of the oil-based drilling fluid and an improvement in its suspension performance. This suggests that the suspension stability of the drilling fluid at room temperature can be improved by reducing the oil-water ratio to ensure the suspension stability of the plugging material during the surface preparation process of the plugging slurry;After the plugging slurry enters the wellbore, as the temperature increases, the viscosity and shear properties of the oil-based drilling fluid decrease significantly. The plugging material can achieve rapid settling (settling time ≤ 24 hours), achieving the goal of "floating on the ground and sinking quickly underground" to ensure safe and efficient plugging construction.Figure 2 shows the evaluation of the sedimentation plug height of oil-based sedimentation plugging slurry with different oil-water ratios at room temperature. It can be seen that the oil-based drilling fluid can maintain stable suspension ability at room temperature of 25℃ under the conditions of oil-water ratios of 60:40, 50:50, and 40:60.
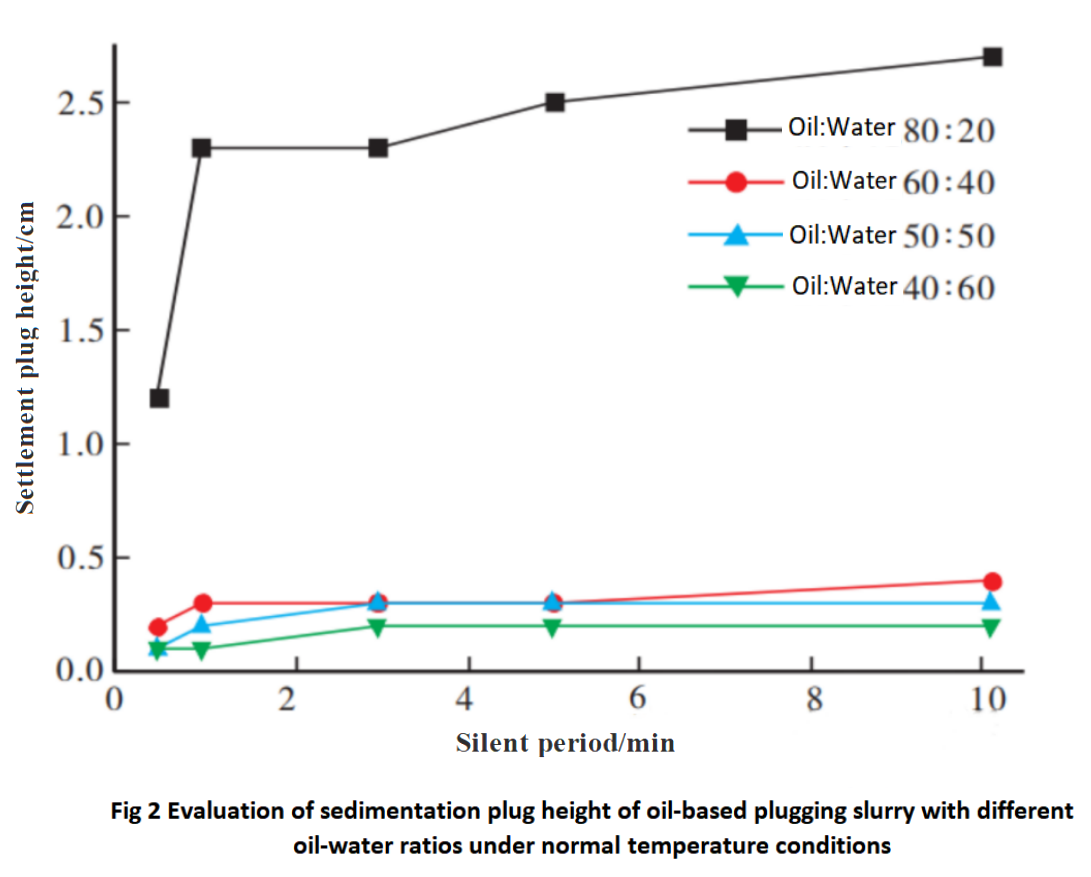
The settlement plugging slurry with the above ratio was heated to 80℃ for evaluation of settlement plugging height, and the results are shown in Figure 3 and Table 5.
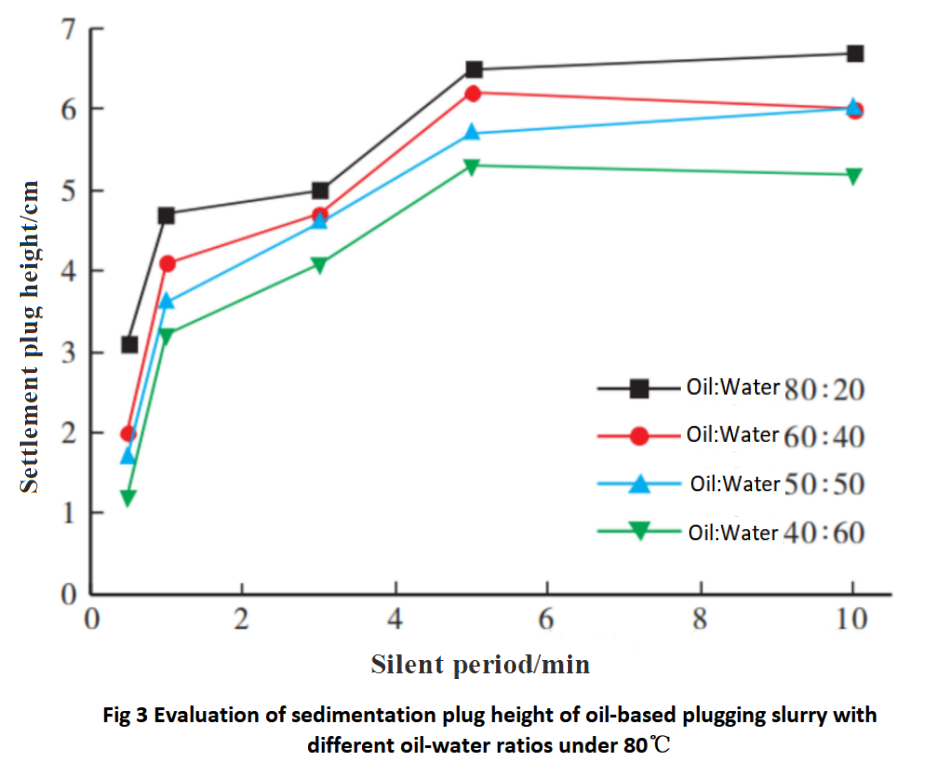
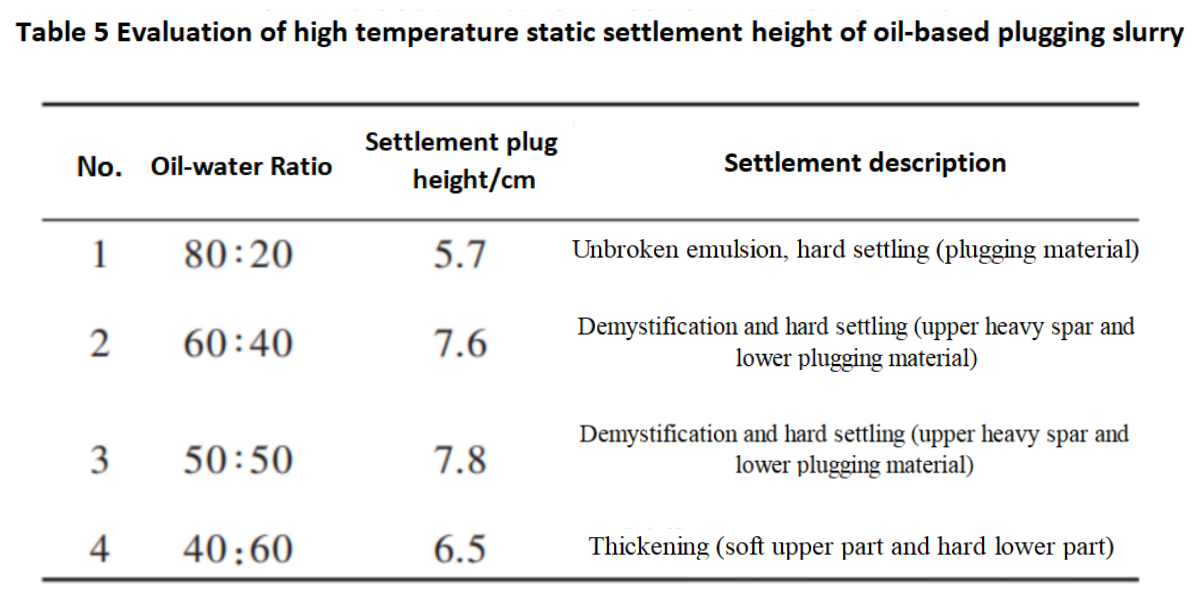
Note: The settlement height is measured after 24 hours of static aging at 160℃.
From the data in Figure 3 and Table 5, it can be seen that after reducing the oil-water ratio, there are different changes in the settling speed and height of the settling plug when heating from 80℃ to 160℃. Among them, the settling speed, settling plug height, and quality are the best at a high temperature of 160℃ when the oil-water ratio is 50:50.
In summary, the use of rigid and synthetic resin based plugging materials as settling plugging materials in oil-based drilling fluids can improve the bottomhole pressure bearing capacity by up to 30MPa. At the same time, by adjusting the oil-water ratio (50:50) and ES (200-300V), the plugging slurry can float at room temperature on the ground, reduce viscosity and demulsify quickly at high bottomhole temperatures, and form the best settling plug height and quality.
2.2 Water based drilling fluid settling and plugging technology
Referring to the plugging materials and formulas used in oil-based drilling fluids, water-based drilling fluids use cutting agents and breaking agents to achieve strong suspension stability under ground conditions and rapid settling under high-temperature downhole conditions.Cutting agents can change the suspension capacity of drilling fluids, while breaking agents can achieve rapid breaking of water-based drilling fluids and cause precipitation of drilling fluids. By introducing cutting agents and breaking agents into the water-based plugging slurry, it ensures that it can float under surface conditions and sink quickly under underground conditions.The cutting agent used in the experiment is XC, a commonly used cutting agent in the Tarim Oilfield site, and the breaking agent is ammonium persulfate, a commonly used agent in the Tarim Oilfield site. The experimental process is the same as that of oil-based drilling fluid, and the experimental results are shown in Figure 4.
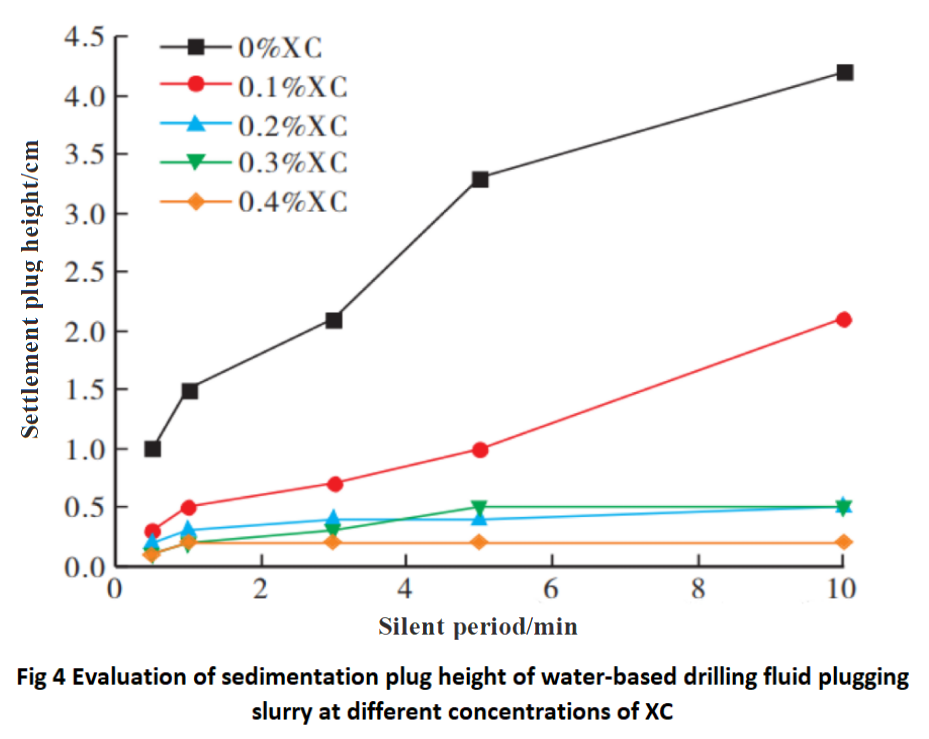
Note: 1. Test temperature condition: 25 ℃; 2. The formula for water-based drilling fluid is 5% soil+0.2% NaOH+3% SMP-3+SNPNH+3% FT-1A+% PRH-1+weighting agent (ρ=2.0 g/cm ³).
From Figure 4, it can be seen that the addition of XC as a cutting agent can improve the suspension stability of water-based sedimentation plugging slurry at room temperature, with the optimal addition amount being 0.2% -0.3%. The experiment added ammonium persulfate as an oxidative breaker to achieve rapid breaking and settling of the settling and plugging slurry at the bottom of the well. The experimental results are shown in Table 6. From Table 6, it can be seen that adding 0.2% breaker at 160 ℃ can quickly form a settling plug.
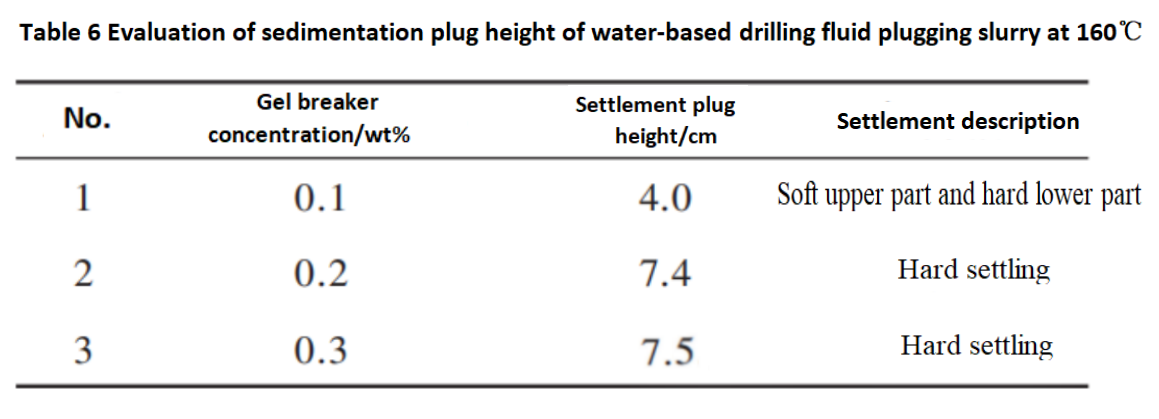
Note: The above settlement plug height is measured after 24 hours of static aging at 160℃.
Based on the above experimental results, adding 0.2% XC, 0.2 wt% demulsifier (added 30 minutes before pumping), and plugging agent to the water-based drilling fluid system can achieve the "floating" of the plugging slurry under ground conditions and "fast sinking" under high-temperature conditions at the bottom of the well, ensuring the optimal quality and speed of the water-based settling plug.
