Intelligent Optimization of Overall Fracturing for Unconventional Reservoirs(Part 3)
2.2 Establishment of Reservoir Model
Usually, the grid size of geological models under the Petrel platform is relatively large (such as a side length of 50m), and the spacing between compression cracks is usually 5-30m. CMG uses local grid refinement to simulate cracks, with the minimum spacing between cracks being one grid size.Therefore, after importing the grid into CMG on the Petrel platform, it is not possible to optimize the seam spacing due to grid size issues.After importing the initial Petrel geological model into CMG, this article fully considers the heterogeneity of the model and uses the local grid refinement function of CMG to perform refinement operations on the grid, thereby achieving the construction of a small grid heterogeneous reservoir model.
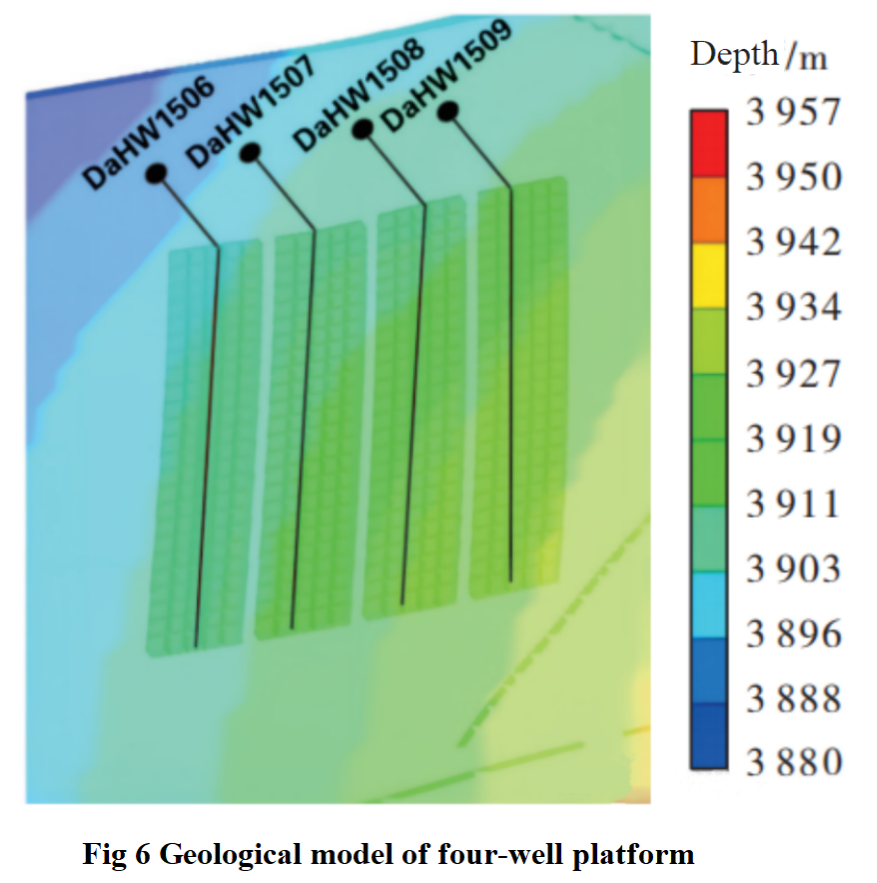
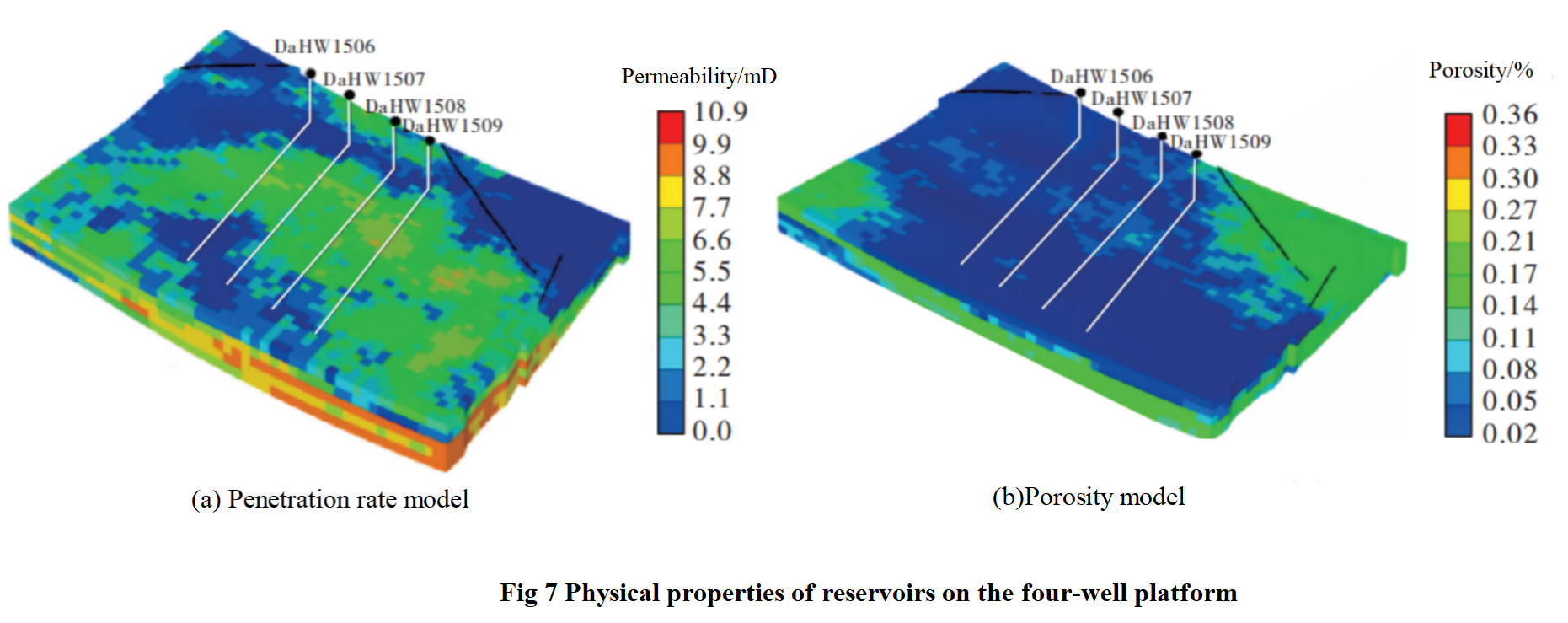
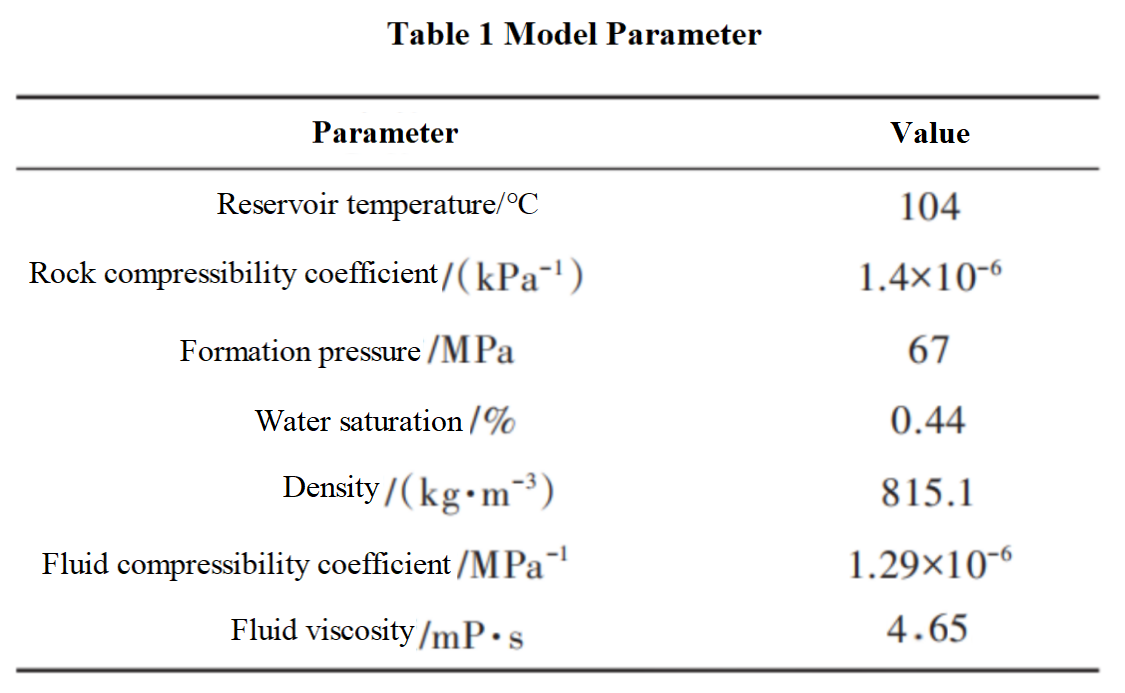
As shown in Figure 6, the number of grids in the reservoir model is 690×3170×5 (I×J×K), and the grid size is 5m×5m×10m. The permeability and porosity distribution of the four well platform model are heterogeneous.As shown in Figure 7, the reservoir is vertically divided into 5 layers, with significant differences in permeability between each layer, mainly distributed between 0.32-10.9 mD. Among them, the permeability of layers 3, 4, and 5 is generally higher than that of layers 1 and 2, which is conducive to oil and gas seepage.The reservoir has strong heterogeneity and relatively large differences in porosity, with a main distribution range of 2% -36%. The porosity of layers 3 and 4 is generally higher than that of layers 1, 2, and 5.Adopting local grid refinement method to establish a layered and staggered flat crack model. Other reservoir properties and fluid parameters are shown in Table 1.
2.3 Model Assumptions and Key Parameters
This article focuses on optimizing the seven dimensional parameters such as well spacing and fracture spacing of the four-well platform to achieve maximum cumulative oil production. Due to the high dimensionality and long computation time of the parameters to be optimized, in order to improve the computational efficiency of the model, the following assumptions are set for the model.
① The geomechanical properties of the four-well platform block are the same;
② The hydraulic fracture properties in the same horizontal well are the same;
③ To reduce the dimensionality of optimization parameters, the optimal crack half length and crack flow capacity were prioritized through single factor analysis.
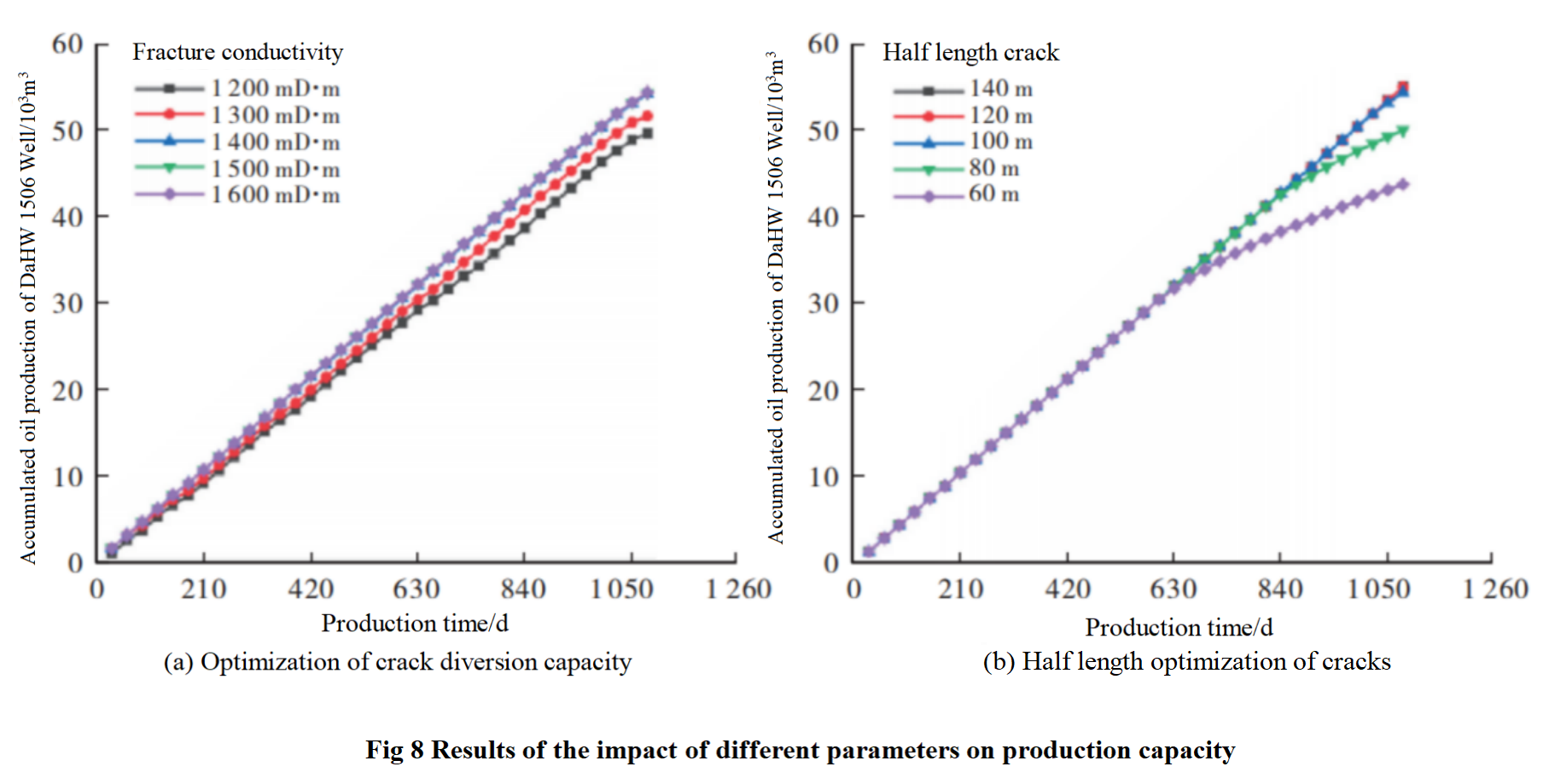
To evaluate the variation in single well productivity with different fracture half lengths and fracture conductivity, the designed fracture half lengths were 60m, 80m, 100m, 120m, and 140m, respectively, while keeping all other parameters consistent. The calculation results are shown in Figure 8.The range of fracture diversion capacity between 1200-1600 mD·m has no significant impact on the cumulative production of a single well. Combined with economic indicators, the best economic benefits are achieved when the diversion capacity is 1400 mD·m.When the half length of the crack is less than 100m, the productivity of the oil well increases significantly with the increase of the crack length; After the half length of the crack is greater than 100m, the production capacity of the oil well tends to stabilize. Therefore, this article sets the half length of the crack on the four well platform to 100m.According to the optimization results, the hydraulic fracture half length of the model is set to 100m, and the diversion capacity is set to 1400mD·m.
3. Comparative Analysis of Optimization Results
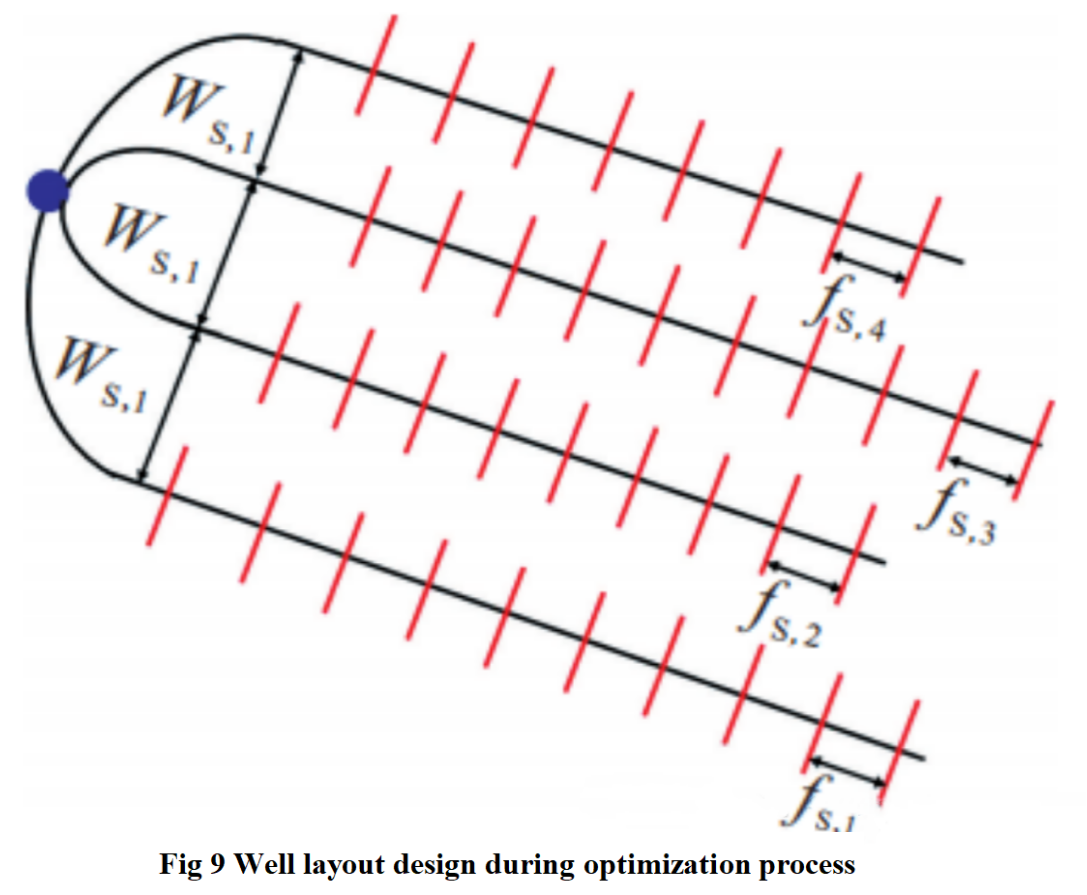
Set the initial values of the three well spacing parameters (WS, 1, WS, 2, WS, 3) of the four well platform to 300m, symmetrically arrange four horizontal wells along the reservoir centerline, and uniformly set 24 hydraulic fractures for each horizontal well. The initial value of the fracture spacing (fS, 1, fS, 2, fS, 3, fS, 4) of the four wells is set to 40m.Figure 9 is a schematic diagram of the well and seam layout scheme, and the optimized parameters and value ranges are shown in Table 2.
3.1 Performance Comparison of Two Algorithms
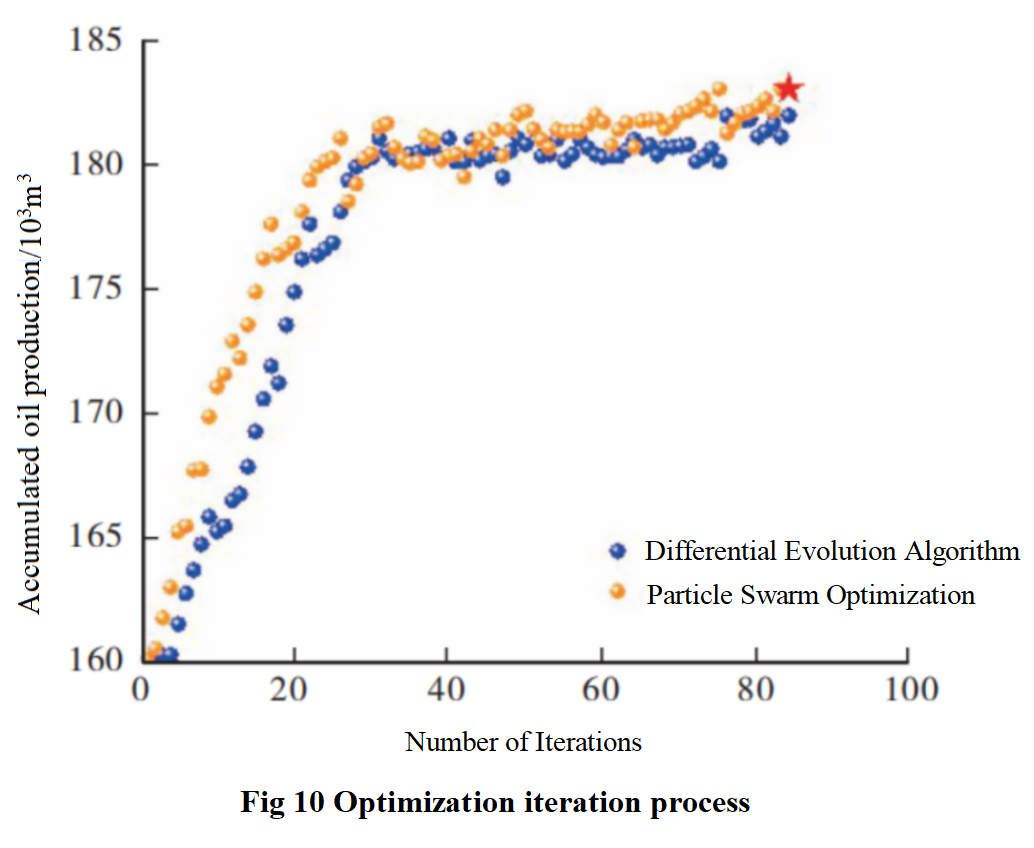
This article uses differential evolution algorithm and particle swarm optimization algorithm for intelligent optimization of well spacing and fracture spacing. The maximum iteration step is set to F90, and the iteration results are shown in Figure 10.The particle swarm algorithm has a faster convergence speed and achieves higher cumulative oil production results. Particle swarm optimization algorithm has fast convergence speed, high optimization accuracy, easy to achieve global optimum, and does not require gradient information and is easy to implement, which can simplify the optimization process.Therefore, particle swarm optimization algorithm is more suitable for optimizing well spacing and fracture spacing in this block.
3.2 Optimized Seven Dimensional Parameter Values
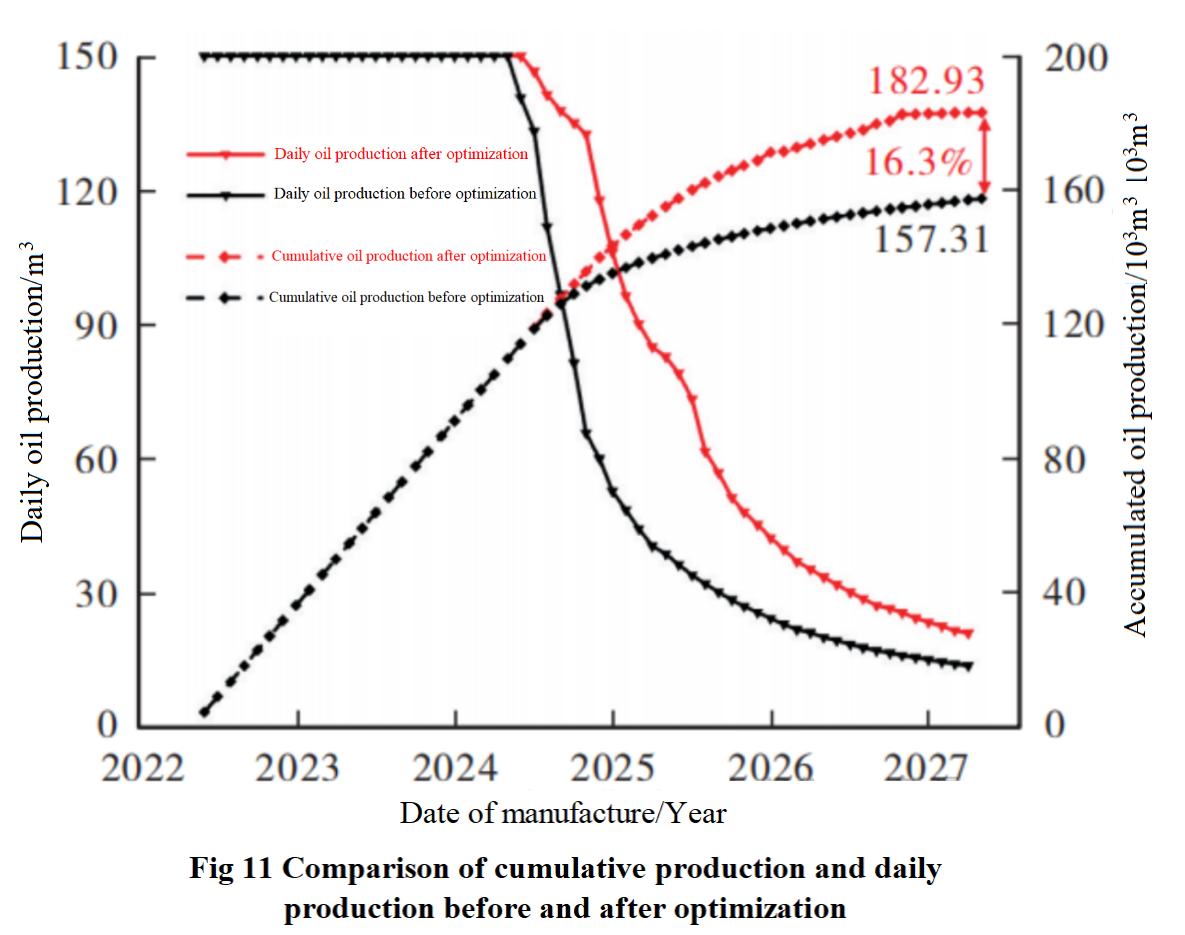
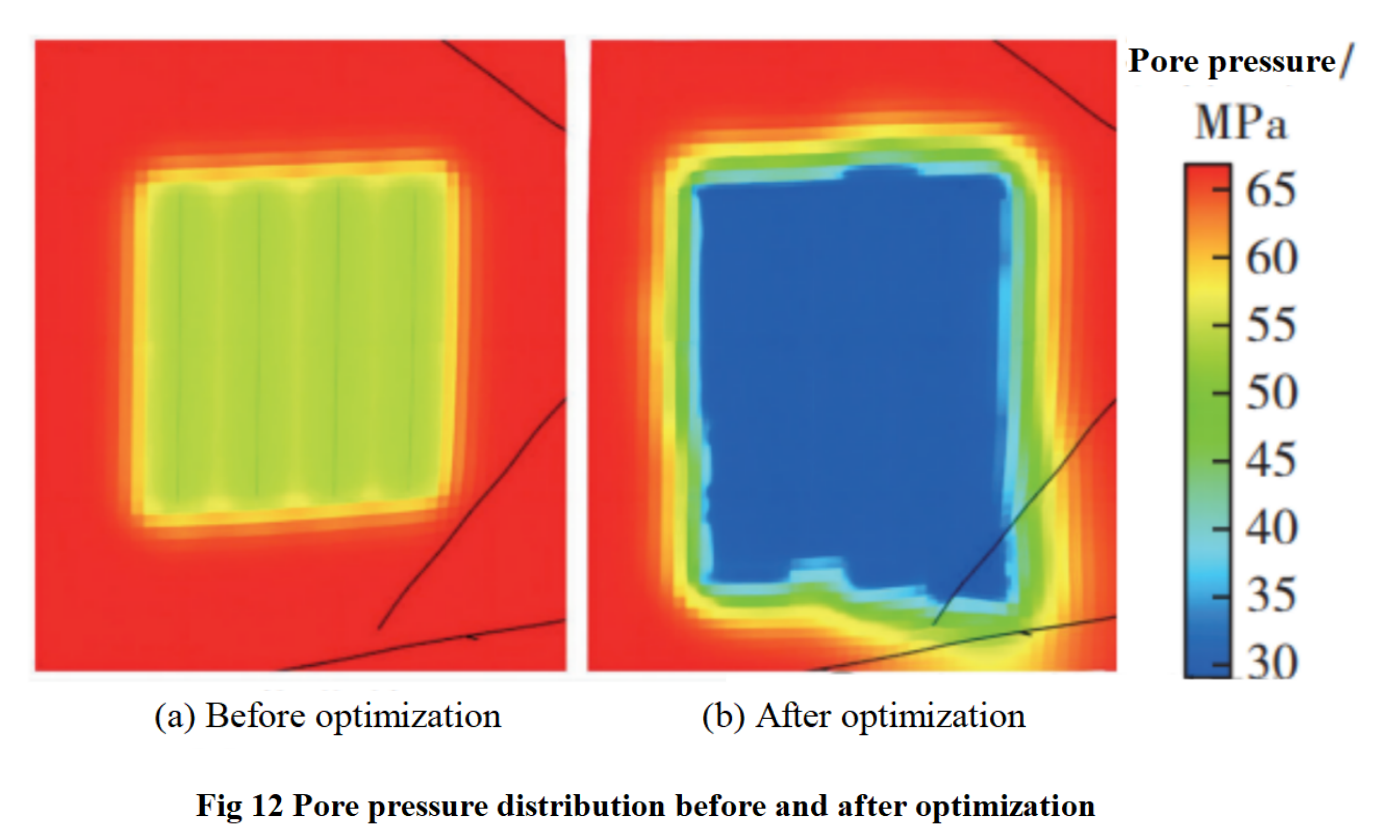
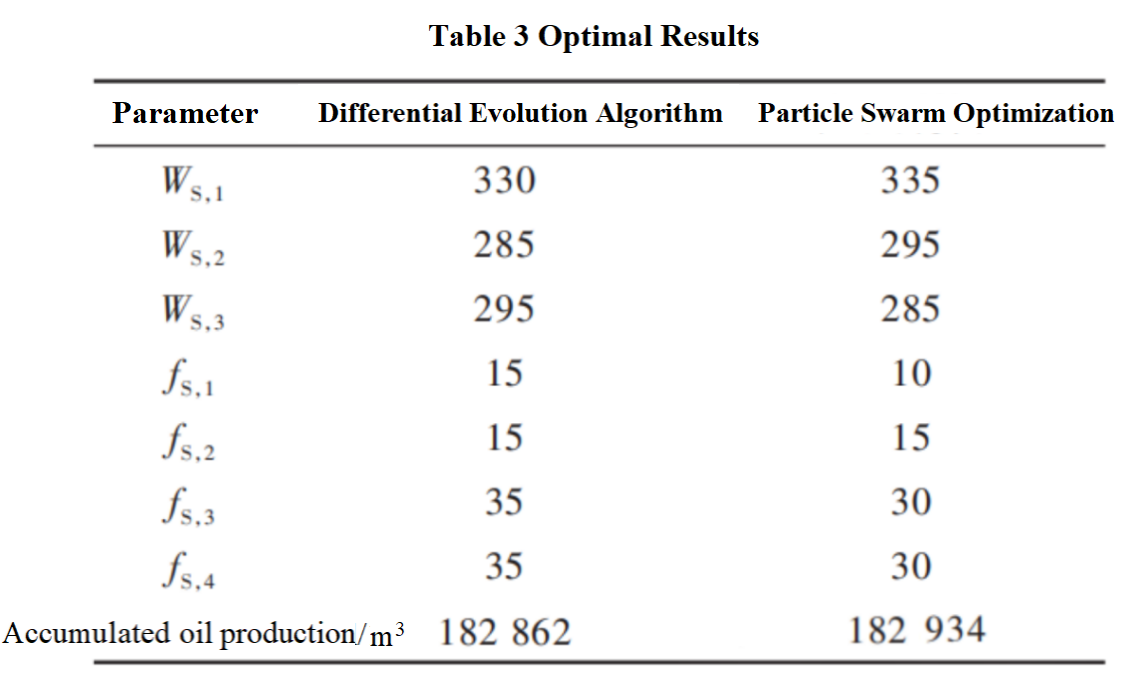
This study mainly optimized seven parameters, including well spacing and fracture spacing, for four wells. The specific parameter values obtained after optimization are shown in Table 3.Figure 11 shows the comparison of production capacity before and after optimization, with the red curve corresponding to the optimal solution and the black curve corresponding to the initial solution. The intelligent optimization method can comprehensively consider the mutual influence between seven dimensional parameters, and the optimization results are more reasonable compared to the single factor analysis method. The stable production cycle of a single well on the four well platform is longer, and the production decline rate is slower. Compared with the unoptimized plan, the cumulative production has increased by 16.3%.From the comparison chart of pore pressure before and after optimization in Figure 12, it can be seen that well spacing and fracture spacing jointly affect the yield size, and they interfere with each other.The spacing is too small, causing production competition, and some areas are repeatedly used, resulting in waste of fracturing operations; The spacing is too large, and some areas cannot be effectively affected, resulting in insufficient utilization of the reservoir.Reasonable spacing between fractures and wells can not only avoid interference between fractures/wells, but also fully transform the reservoir, improve the fracture controlled reserves of the reservoir, and increase the coverage area of the pore pressure field. The production effect of the optimized plan is better than that of the initial plan.
4. Conclusions
By coupling intelligent optimization algorithms and fracturing well group reservoir simulation platform, synchronous optimization work was carried out on the well spacing and fracture spacing of a four well platform in a typical block of Mahu conglomerate reservoir. The main conclusions are as follows.
1). Importing the fine geological model established by the Petrel platform into the CMG reservoir numerical simulation platform, a well group fine fracturing productivity prediction model is established. Combined with intelligent optimization algorithms, high-dimensional parameters of well group fracturing can be intelligently optimized.
2). The matching between well spacing and fracture spacing significantly affects the effectiveness of well group transformation. After optimization, the fracture spacing of the four well platforms was 10m, 15m, 30m, and 30m, and the well spacing was 335m, 295m, and 285m, respectively. The optimized well group productivity increased by about 16.3% compared to the basic model.
3). Comparing two intelligent optimization algorithms, particle swarm optimization algorithm has faster convergence speed and higher cumulative oil production. Particle swarm optimization algorithm is more suitable for parameter optimization of target blocks.
