Intelligent Optimization of Overall Fracturing for Unconventional Reservoirs(Part 2)
1.3 Plane Crack Model
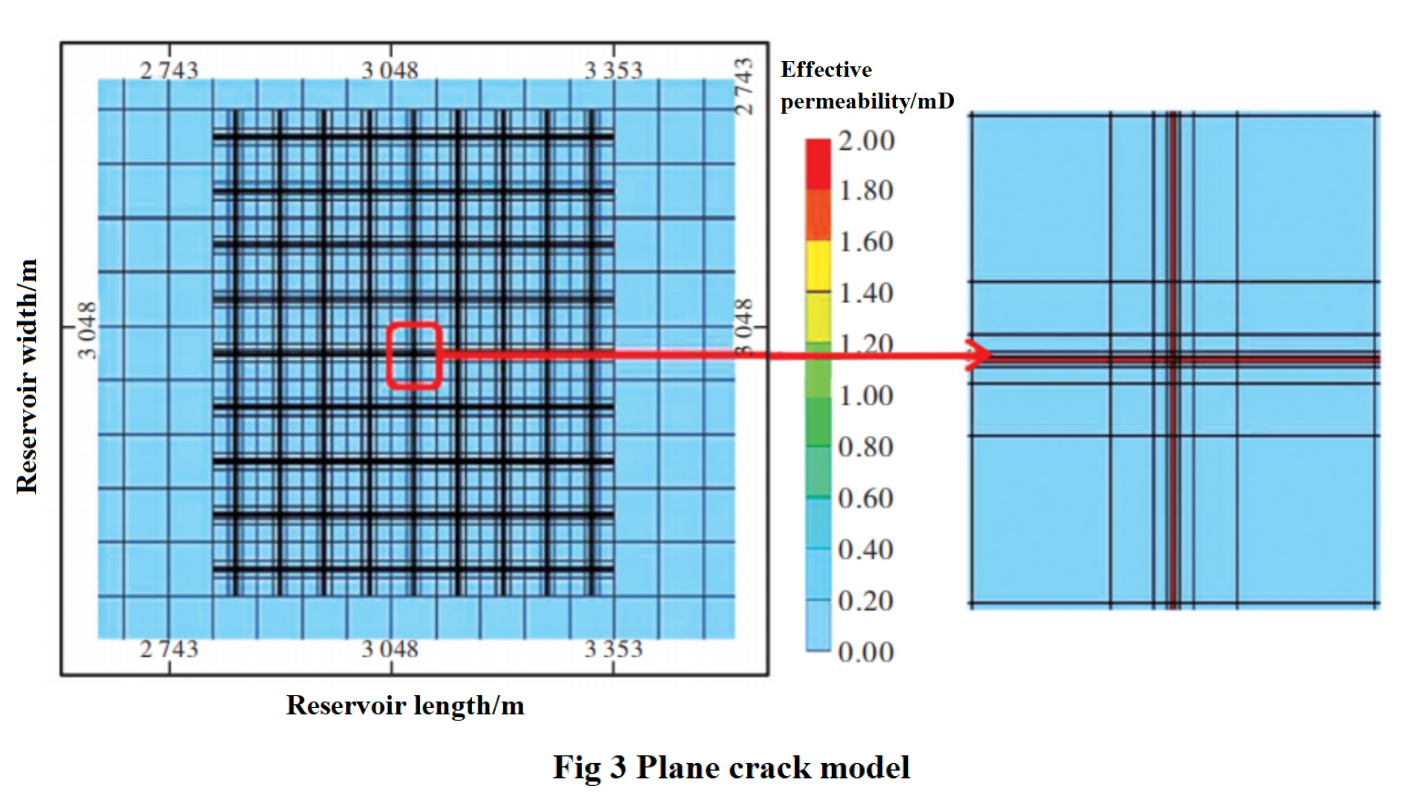
In the process of reservoir simulation, it is necessary to consider production interference between multiple fractures, non Darcy flow in fractures, and differences in fracture length and conductivity between different fractures.This article chooses the GEM module in the CMG reservoir numerical simulator to simulate the reservoir, which can consider non Darcy flow and production interference between fractures.The planar crack model in GEM simulator can accurately simulate the instantaneous behavior of oil and gas flow between multiple cracks and between matrix and cracks, as shown in Figure 3.The grid intersecting the plane crack and the wellbore has been logarithmically encrypted in both directions to more accurately simulate fluid flow inside the wellbore and crack.The red color represents the fracture zone of the reservoir, with a default width of 0.6096m in GEM, while the actual fracture width is 0-10mm.In order to simulate narrow cracks of actual width in a wider crack zone, assuming that the actual crack conductivity is equal to the fracture conductivity of the red crack zone used in GEM, the effective permeability Keff of the red crack zone can be calculated using formula (1).
.png)
In the formula
Keff—The effective permeability of the red crack zone, mD;
Kactual—Actual crack permeability, mD;
Wactual—Actual crack width, m;
Wblock—The width of the red crack zone, m.
1.4 Algorithm Optimization Comparison
Differential evolution algorithm evolved from early genetic algorithms and is an efficient continuous variable global optimization algorithm.This algorithm uses multiple iterations to automatically enrich the population while selecting excellent individuals and eliminating inferior individuals, making the solution of the problem approach the global optimum. It has the advantages of simple principle and strong robustness.Its most prominent feature is adaptive mutation operation, which can continuously adjust the difference vector factor of mutation disturbance with evolution, balance the global and local search capabilities of the entire algorithm, and enable the optimized results to reach the global optimum.Particle swarm optimization algorithm is a commonly used optimization algorithm, which was developed inspired by the foraging behavior of bird flocks. In particle swarm optimization, each individual is treated as a particle and assigned a randomly generated initial position and velocity in the solution space. Each particle constantly updates its position and velocity, and adjusts based on its historical best position and global best position to find a better solution.Particles iterate continuously in the search solution space until they reach a predetermined number of iterations or a specific optimization goal.This algorithm does not require gradient information, has fast convergence speed, and is easy to implement.As this optimization is a high-dimensional parameter optimization, the overall optimization process takes a long time, and it is necessary to choose an algorithm with simple operating principles, short time consumption, and the ability to obtain the global optimal solution.Differential evolution algorithm and particle swarm optimization algorithm have good performance in optimizing high-dimensional parameters and operating time costs, while also having good robustness and stability. Therefore, this article chooses differential evolution algorithm and particle swarm optimization algorithm to optimize the above parameters. The flow of the two optimization algorithms is shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5.
1.5 Objective Function
Considering the long-term production effect, this article selects the cumulative oil production f (x) over the next five years as the objective function to obtain the parameter combination that maximizes the cumulative oil production, as shown in formula (2).
.png)
In the formula
X*—The feasible vector set that can maximize the objective function;
f(x)—The oil well productivity obtained through iterative calculation, m3;
x —A seven dimensional vector containing all control variables.
The optimization process is to find a vector set Xi = X1, X2, …, Xi that maximizes the objective function value while satisfying the boundary constraints, and this vector set is the optimal solution.Integrated fracturing intelligent optimization refers to synchronous optimization of seven dimensional parameters, including the spacing between three wells and four fractures, in the four well platform.Conventional fracturing optimization usually adopts the single factor analysis method, which controls other parameters to constant values and only changes one parameter for optimization. The optimization result can only be a local optimal value and cannot consider the mutual influence between various parameters.This article innovatively adopts multi platform fusion and intelligent optimization algorithms to synchronously optimize the seven dimensional fracturing parameters, and obtains the best matching well spacing and fracture spacing combination for the four well platform.The well spacing and fracture spacing affect the degree of production interference and the control volume of fracturing transformation, thus closely related to cumulative oil production.Previous studies have chosen fracturing transformation volume, daily oil production, or net present value as objective functions, but these objective functions are difficult to directly reflect the matching relationship between well network and well spacing.
2. Reservoir Characteristics and Optimization Model Establishment
2.1 Reservoir Overview
The platform of Well 4 is located in Well Block Da13 of Mahu Sag in the Junggar Basin. The target horizon for horizontal well drilling is Baier Member of Baikouquan Formation of Triassic System, with sand body thickness of 21.2m and oil layer thickness of 11.3m.Two interlayers are developed within the oil reservoir, with the upper layer being a physical interlayer with a thickness of 0.3m; The lower part is a mudstone interlayer with a thickness of 0.3m.The oil reservoir in the well area where the platform is located is buried deep, with complex structures and developed faults. The distribution of geostress is unclear, and the extension law of hydraulic fractures is complex. Natural fractures are not developed.
